How long does Ciprofloxacin take to treat bacterial infections?
Ciprofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic medication used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It belongs to the Fluoroquinolone group of medications and is effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, infectious diarrhea, bone infections, and ocular with ear-related infections are among the wide range of systemic complications that respond well to Ciprofloxacin BNF.
How quickly does Ciprofloxacin kick out bacterial infections?
Ciprofloxacin 500 mg may take a few hours to a few days to start showing effects, depending on the condition for which it is used. In addition to the strength of the medication, the patient’s systemic conditions and medical requirements were advised.
Ciprofloxacin is available in several forms, including immediate oral release, extended oral release, as an ophthalmic solution for the eyes and ears, and intravenous form for deep-seated infections requiring a concentrated antibiotic. Immediate-release Ciprofloxacin works faster than extended-release formulation and starts working within a few hours. Topical applications of the medication work within 1-2 hours, but it takes a few days to observe the visible effects.
Key points associated with Ciprofloxacin
- Open-label, non-comparative trial in adult women with uncomplicated UTI has demonstrated a rapid improvement in UTI symptoms severity within 6-24 hours. They were able to return to work within 24 hours after treatment with extended-release Ciprofloxacin.
- Extended-release Ciprofloxacin at a dose of 1,000 mg once daily was as safe and effective as conventional treatment with 500 mg ciprofloxacin twice daily, each given orally for 7 to 14 days in adults with urinary tract infection or acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis with symptoms of burning on urination, vomiting, nausea, and flank pain.
- Ciprofloxacin at a dosage of 100 mg given for three days was the minimum effective dose for treating uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women.
- Ciprofloxacin has shown a positive response to the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis, a bone infection caused by the staphylococcus bacteria found on the nose and skin of healthy individuals. The duration of treatment in trial cases was approximately 76 days with a follow-up therapy of 3-13 months unaccompanied by significant side effects or risks.
- Regarding the use of Ciprofloxacin in conditions of bacterial vaginitis, researchers have found that treatment of Ciprofloxacin did not affect the profile of lactobacillus colonization, nor did it produce adverse effects or produce symptoms referred to the vagina. Moreover, in conditions of candida-induced bacterial vaginitis, neither Ciprofloxacin nor other previously effective drugs affected the prevalence of C. Albicans.
- A short-course Ciprofloxacin regime for treating enteric fever or typhoid caused by the Salmonella Typhi bacteria can prove effective. It took usage of Ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily for seven days in clinical studies for the symptoms to recede satisfactorily. It took 10-14 days at the same dose in mild drug-resistance cases to obtain the required therapeutic benefits.
- Clinical studies on 25 acutely ill patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia showed 100% successful results with oral Ciprofloxacin. 12 out of 25 received 750 mg of Ciprofloxacin orally every 12 hours for 3-6 days, followed by 500 mg of oral medication twice daily for 4-7 days. The remaining 13 patients received 500 mg of Ciprofloxacin orally for 8-15 days. Apart from successful treatment, no superinfections occurred, and there was no development of resistance.
Ciprofloxacin safety
The safety of Ciprofloxacin tablets was established on a database comprising 9,473 well-documented treatment courses worldwide. The daily dosages ranged between 200 and 2,000 mg orally. Thirty-eight percent of the patients received doses between 1 and 10 mg/kg body weight, 46 percent between 11 and 20 mg/kg, and the remaining 16 percent more than 20 mg/kg body weight daily. Ciprofloxacin was administered to 4,214 women (45 percent) and 5,252 men (55 percent), with treatment duration ranging from less than two days to more than 90 days. The total incidence of side effects for the treated patients was 9.3 percent, with mild or moderate adverse reactions. Serious side effects were reported for only 6 percent, and the incidence of severe reactions was 0.6 percent.
Ciprofloxacin treatment was discontinued in 1.5 percent % of cases primarily due to gastrointestinal reactions. The worldwide data from clinical trials with oral and intravenous Ciprofloxacin from the study mentioned above and other clinical trials demonstrate that the drug is relatively safe, and the Ciprofloxacin side effects are usually mild or moderate in intensity and are reversible.
If you do not take the required precautions or use it injudiciously, things can go wrong.
Factors impacting the effect of Ciprofloxacin
Resistance
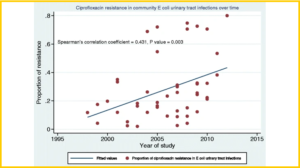
Anti-microbial resistance to Ciprofloxacin, especially E.coli, is on the increase. The resistance is higher in hospital-acquired E.Coli UTI compared to community-acquired E.Coli UTI. In addition; developing countries are at a greater risk.
A scatterplot of Ciprofloxacin resistance in 47 studies reporting on community-acquired UTIs has shown a statistically significant rise in resistance over time. The findings are comparable to individual studies assessing urinary E.Coli resistance to Ciprofloxacin in hospital and community settings. This can affect the medication’s effectiveness considerably, causing an increased spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in communities.
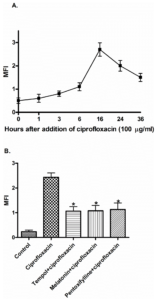
Drug interactions
Ciprofloxacin works by interfering with the replication and transcription of bacterial DNA, increasing oxidative stress and, subsequently, death/destruction of the bacterial cells. Drugs with strong antioxidant activity like tempol, melatonin, and pentoxifylline might interfere with Ciprofloxacin’s antibacterial activity and considerably diminish its effectiveness.
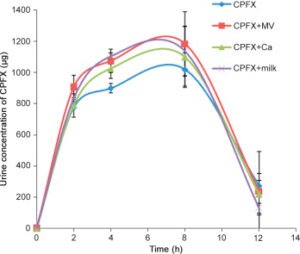
Food interactions
Research has shown that elimination of Ciprofloxacin can increase significantly when co-administered with multivitamins, calcium tablets, and milk in the order of multivitamin>milk> calcium, in contrast to Ciprofloxacin release when administered alone. A 2-hour window between calcium /milk and Ciprofloxacin and a 4-hour window between multivitamin and ciprofloxacin intake to stay on the safe side.
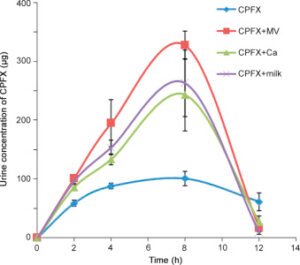
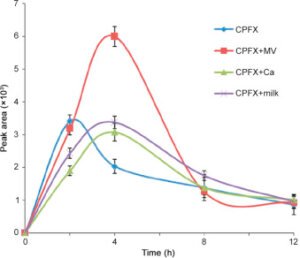
Take-away points
- Ciprofloxacin works best on urinary tract infections, but unfortunately, growing misuse is giving rise to problems of drug resistance that could prove problematic in the future.
- Using Ciprofloxacin in typhoid, osteomyelitis, and vaginal infections takes a slightly extended period but yield positive results without adverse reactions.
- Ciprofloxacin has a safe profile and can be used without severe complications or side effects.
- It is essential to avoid milk, calcium supplements, and multivitamins concomitantly with the medication.
- Drug interactions can affect its absorption rate and must be avoided at all costs.
References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16083534/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14713799/
https://www.karger.com/Article/Pdf/294862
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7864704/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1474262/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2732778/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2732778/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2686432/
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/5/1/28/htm
https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-015-1282-4
Related Post
Buy Ivermectin
Free Express Delivery (Royal Mail)
Dispatched Within 24 Hours
Delivery Within 3-5 Business Days