Amoxicillin 500mg – The Proven Mechanism Of Action And All Indications
Introduction
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication with a wide range of antibacterial properties that extends into pathogens of viral and fungal nature. It is hugely popular because of its quick onset of action and ability to work successfully in monotherapy and as an adjunctive medication. Amoxicillin belongs to the class of beta-lactam antibacterials that get their name from containing a beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure. Amoxicillin was discovered in 1958 and approved for use in 1974 in the States and in 1977 in the United Kingdom. It is often confused with Ampicillin because of the similar nomenclature and class despite being different in terms of the more lipid-soluble nature of Amoxicillin which provides it the advantage of having a quicker onset of action.
Mechanism of Action
It’s essential to understand the structure of the drug to have a better idea about its mechanism. Amoxicillin, by nature, is an amino-penicillin created by adding an extra amino group to the molecular structure of Penicillin to provide added effects and battle antimicrobial resistance effectively
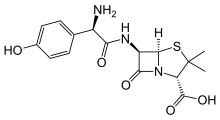
Image Source:- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amoxicillin
Aminopenicillins are broad-spectrum penicillins designed to be used in a broader range of bacterial conditions. Though slightly less active against Gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria than Penicillin, they have greater activity against Gram-negative bacteria and are thus more effective in pneumonia, open wounds, surgical sites, and bloodstream infections where Penicillin ceases to be optimally effective.

Image Source:- https://www.animalresearch.info/en/drug-development/drug-prescriptions/amoxicillin/
Because of the similar core structure, both Amoxicillin and Penicillin have similar mechanisms of action, and the medication binds to the penicillin-binding proteins in the pathogen’s body to carry out its therapeutic effects. The result is an inhibition in the transpeptidation process used to create cross-links (covalent bonds) between peptidoglycan molecules in the bacterial cell wall and prevent new cell wall formation.

Image Source:- https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Biochemistry-and-Action-of-Clavulanic-Acid-Cole/d88ad8ba41dab9ea4420f3e7e1395f0ad8cfbce5/figure/0
Without a cell wall, a bacterial cell becomes vulnerable to outside water and molecular pressures, which causes the cell to die quickly. Because mammalian cells do not have a peptidoglycan cell structure, the inhibition of cell wall peptidoglycan biosynthesis successfully destroys the microbial pathogen without adverse reactions in the human body.
Besides exerting its solo effects on the bacterial cells, the medication works as successfully when combined with Clavulanic Acid for added antibacterial benefits. Clavulanic Acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that binds to the beta-lactamase enzyme to inactivate it. Beta lactamases are enzymes that enable bacteria to resist the antibiotic activities of drugs like Penicillin, cephalosporins, cephamycins, and carbapenems.

Image Source:- https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Biochemistry-and-Action-of-Clavulanic-Acid-Cole/d88ad8ba41dab9ea4420f3e7e1395f0ad8cfbce5/figure/4
Clavulanic Acid creates a symbiotic effect with beta-lactam antibiotics like Amoxicillin and successfully prevents bacterial resistance through the beta-lactam ring composing the core of its structure.
Studies have shown that Amoxicillin-Clavulanate, when traditionally administered in regimens of 500 mg Amoxicillin with 125 mg Clavulanate on an eight-hourly basis, is an effective option for conditions of acute bacterial sinusitis. The effectiveness of amoxicillin-clavulanate in these conditions is as effective as other potent antibiotics like Cefuroxime Axetil and Ceftibuten Dihydrate and recommended as a first-line treatment option like other combination medications like trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Some of the other indications of Amoxicillin therapy are:-
Indications
One of the most important indications of Amoxicillin is in treating Streptococcus pneumoniae, the chief pathogen behind Pneumococcal disease/ Pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae is spread from person to person by inhaling or direct exposure to the bacteria droplets through coughing or sneezing from an infected person. It is one of the most common infections in the States, with an incidence of 5-6/100000 in adults that increases sixfold in older people and children. The symptoms of pneumonia usually start with fatigue, cough, and fever, which in turn progress into symptoms of chest pain and labored breathing and require hospitalization.
In such conditions, Amoxicillin effectively works on the pathogen and provides symptomatic relief to the patient. The drug in vivo has proved to have successful results, especially in children, and reduced the mortality rate with the time spent in hospitalization. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends oral Amoxicillin in fast breathing pneumonia ( the term used for respiratory rate of at least 50 breaths in an infant 2-11 months or at least 40 breaths or more in a child 12-59 months) in doses of 50mg for at least three days while ensuring that they are not HIV positive or immunodeficient. Other trials have demonstrated that the drug can be used in lower doses as a monotherapy for improving cough symptoms and allowing the patients quality sleep previously impaired by pneumonia symptoms.
Additionally, the drug is used as a second treatment line for tonsillitis conditions not responding to or intolerant to Penicillin. Lab studies have shown that a daily dose of Amoxicillin is similar in effectiveness to other dosing schedules every 6, 8, or 12 hours of penicillin V.


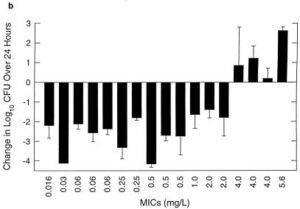
Animal studies of Amoxicillin and amoxicillin/clavulanate against multiple strains of S. pneumoniae
Image Source:- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC105836/
Recently Amoxicillin PULSYS has been introduced to provide a lower treatment dose, once-daily alternative to currently approved amoxicillin and penicillin regimens for the treatment of adolescents/adults with pharyngitis and tonsillitis. Trials showed a success rate of 76.6% in bacterial eradication in Amoxicillin PULSYS compared to 88.5% shown by Penicillin.
Despite the trial not showing the required success, the drug can be considered an alternative treatment option in conditions of unavailability of Penicillin or the use of which produces hypersensitivity reactions of moderate intensity.
Amoxicillin indication in typhoid
Typhoid affects 3.6 persons per population and has a high mortality incidence, with the WHO estimating the disease burden to be 11-20 million cases and 128 000–161 000 yearly deaths caused by the pathogen. Ciprofloxacin and Ofloxacin are usually the first lines of treatments for the condition, but recently, with the growing cases of chloramphenicol resistance exhibited by S.Typhi it is being regarded as an alternative treatment option because of its benefits against the drug resistance mechanism of pathogens. A study by Calderon reported that all typhoid patients administered with Amoxicillin recovered fully after five days. In other clinical trials, the use of Amoxycillin showed equal effectiveness to intravenous Ampicillin in curing typhoid caused by chloramphenicol-resistant S. typhus.
Most importantly, It can be used in pregnant women.
Pregnant women in the first trimester are at an increased risk of tonsillitis and urine infections and require prompt medical intervention as the pathogens can be detrimental to the fetus’s health. The growing baby and uterus also reduce a woman’s lung capacity, which puts more stress on lung function and increases the incidence of pneumonia and other chest infections.
It is considered a category B drug by the FDA and is thus considered safe to take while pregnant. Exposure to Amoxicillin and Amoxicillin combined with clavulanic Acid is easily tolerated and does not lead to complications related to organ systems.
Read More:- Is it safe to take Amoxicillin 500mg during pregnancy?
Conclusion
The advanced structure of Amoxicillin and its effectiveness against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria makes the drug a practical option for many infections and preferable over other medications to which the pathogens build resistance over time.
In addition to producing favorable effects for pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes and Enterococcus spp, it has even shown effectiveness for Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, Actinomyces spp., Clostridium species, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., and Corynebacteria species that can permanently damage the gastrointestinal system and lining of intestines and prove life-threatening. Using it at regulated doses would be best as higher strengths can damage the kidneys and other vital organs
Reference Links:-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amoxicillin
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/000348949510410s03?journalCode=aora
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17963430/
https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-abstract/129/Supplement_2/S219/908447?redirectedFrom=fulltext
Related Post
Buy Ivermectin
Free Express Delivery (Royal Mail)
Dispatched Within 24 Hours
Delivery Within 3-5 Business Days